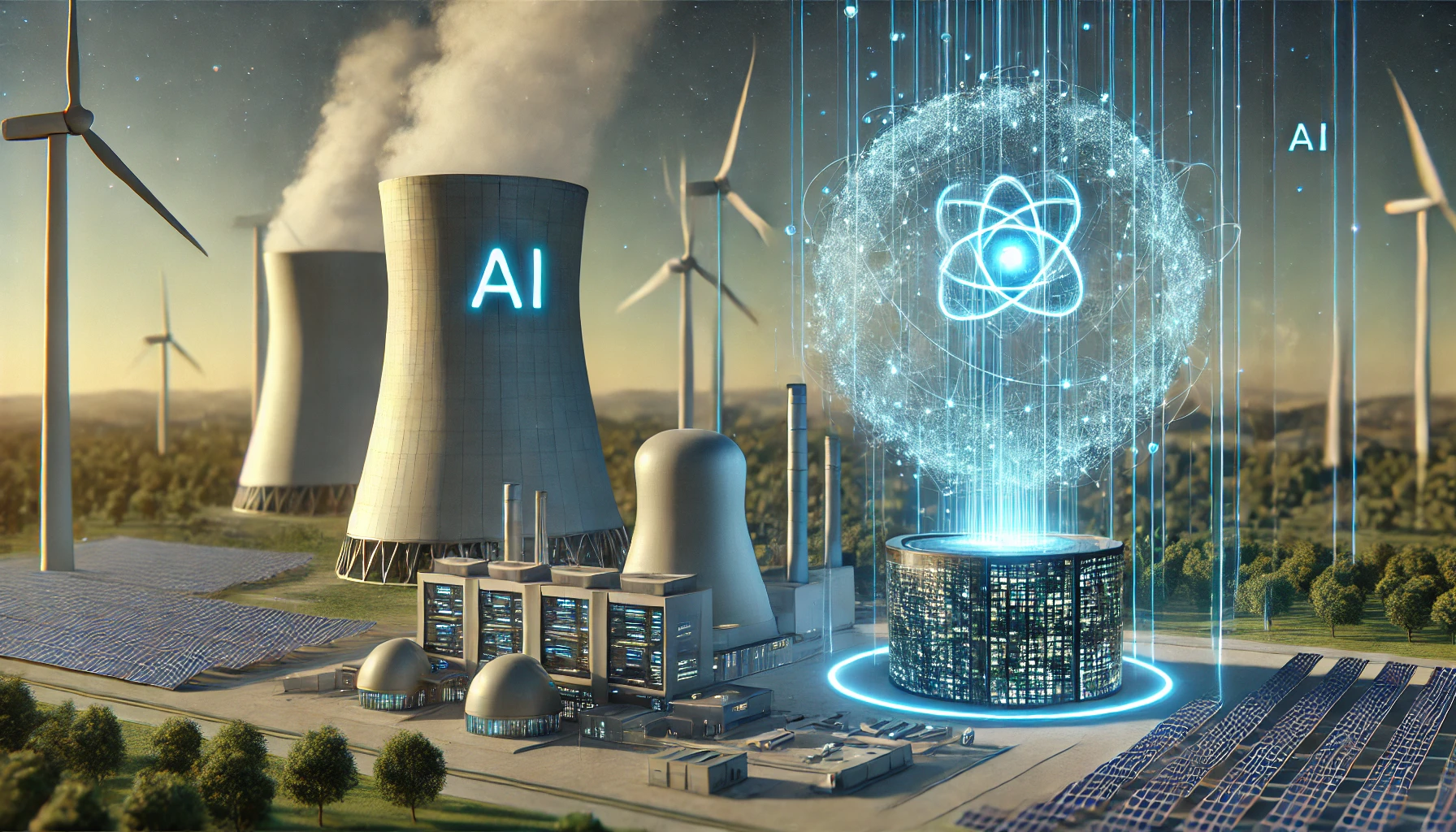
Google’s Groundbreaking Deal to Build Small Nuclear Reactors for AI: A Game-Changer for Energy and Technology
In a bold move, Google has recently signed a deal with a startup to construct small nuclear reactors designed to power its growing AI infrastructure. As AI continues to develop and demand higher energy capacities, Google is exploring innovative ways to ensure a sustainable, scalable, and reliable power source. This collaboration highlights the tech giant’s forward-thinking approach to addressing the significant energy consumption required for advanced computing technologies.
Why Nuclear Reactors for AI?
The increasing demand for artificial intelligence (AI) applications requires an enormous amount of computational power. Data centers, which house servers and AI systems, already consume vast amounts of electricity, and the need for energy is only growing. As AI models like Google’s large language models (LLMs) scale up, the energy demands grow exponentially.
Traditional energy sources may not suffice in meeting this future demand in a sustainable way, particularly with the global focus on reducing carbon emissions. Nuclear power offers a low-carbon, reliable solution to meet Google’s future energy requirements. By investing in small nuclear reactors (SMRs), Google can secure a steady supply of clean energy while reducing its carbon footprint.
What Are Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)?
SMRs are an emerging class of nuclear reactors that are more flexible, cost-efficient, and safer than traditional nuclear power plants. These reactors are designed to be built on a smaller scale, with the ability to be transported and assembled more quickly than large-scale nuclear plants. SMRs produce less nuclear waste and are easier to integrate into existing power grids, making them an attractive option for companies seeking sustainable and scalable energy solutions.
By adopting SMR technology, Google can:
- Reduce Carbon Emissions: Nuclear energy is one of the most powerful zero-carbon energy sources available.
- Enhance Energy Independence: By having its own power-generating facilities, Google can decrease reliance on traditional grid-based electricity, which is prone to fluctuations and blackouts.
- Increase Reliability: SMRs provide a consistent and stable energy supply, essential for running AI systems 24/7 without disruption.
The Role of AI in This Power Shift
Google is at the forefront of AI development, and the infrastructure needed to support machine learning models is growing. From running large-scale neural networks to training advanced models, powering these systems demands constant and vast amounts of energy. The partnership to build nuclear reactors signals a strategic move to future-proof its AI capabilities by ensuring access to continuous, clean energy.
In turn, AI could also contribute to optimizing nuclear power generation, as machine learning algorithms can enhance operational efficiency, monitor systems for safety, and predict maintenance needs.
What This Means for the Energy Sector
Google’s decision to use SMRs could trigger a broader shift in how tech companies approach their energy needs. The collaboration could also accelerate the development and adoption of nuclear technology in private enterprises. Additionally, this move signals confidence in SMR technology, which, if successful, could influence other major tech companies to explore similar solutions.
Google’s SMR initiative not only positions it as a pioneer in the fusion of advanced AI and nuclear technology but also sets a precedent for sustainability and energy innovation in the tech industry. By committing to this nuclear-powered future, Google reinforces its leadership in the development of cutting-edge technology while addressing one of the most pressing global challenges: reducing carbon emissions.
The Road Ahead
The timeline for the deployment of these nuclear reactors is yet to be fully realized, but the commitment marks a new phase in the tech industry’s pursuit of sustainable energy solutions. As Google pushes the boundaries of AI, this energy partnership could shape the future of both AI technology and the nuclear energy landscape.
This venture emphasizes that the future of AI is not only about advancing algorithms and machine learning but also about addressing the practical challenges of infrastructure, sustainability, and energy supply.
In conclusion, Google’s investment in small nuclear reactors represents a visionary approach to powering the future of AI. As AI and energy demands grow in tandem, such innovations are crucial for a sustainable and technologically advanced future.