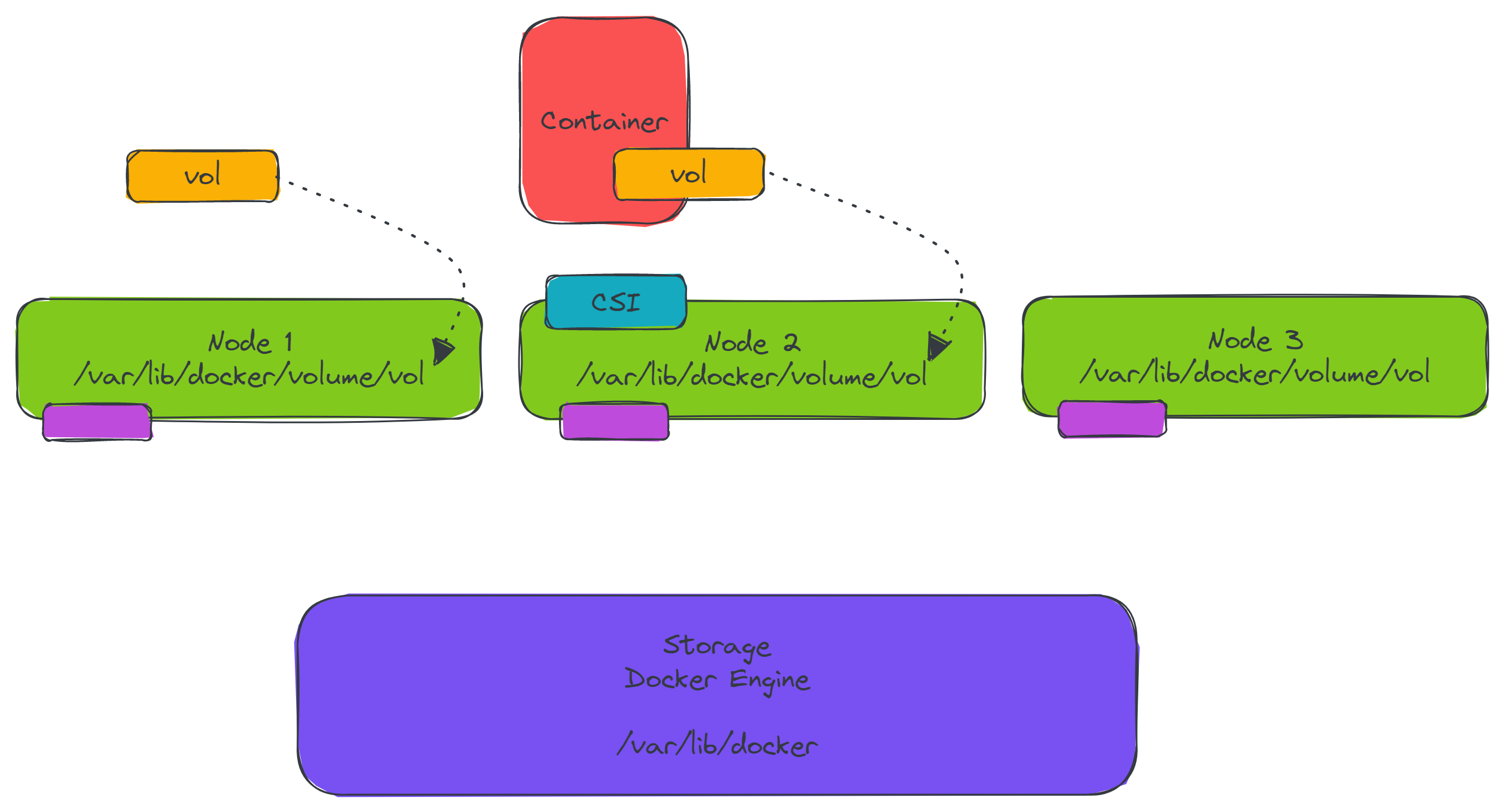
Storage in a Cluster for Docker Swarm Using Sshfs
 Install the
Install the vieux/sshfsplugin on all nodes in the swarm.docker plugin install --grant-all-permissions vieux/sshfs- Set up an additional server to use for storage. You can use the
Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic Beaver LTSimage with a size ofSmall. On this new storage server, create a directory with a file that can be used for testing.mkdir /home/cloud_user/external echo External storage! > /home/cloud_user/external/message.txt - On the swarm manager, manually create a Docker volume that uses the external storage server for storage. Be sure to replace the text
<STORAGE_SERVER_PRIVATE_IP>and<PASSWORD>with actual values.docker volume create --driver vieux/sshfs \ -o sshcmd=cloud_user@<STORAGE_SERVER_PRIVATE_IP>:/home/cloud_user/external \ -o password=<PASSWORD> \ sshvolume docker volume ls - Create a service that automatically manages the shared volume, creating the volume on swarm nodes as needed. Be sure to replace the text
<STORAGE_SERVER_PRIVATE_IP>and<PASSWORD>with actual values.docker service create \ --replicas=3 \ --name storage-service \ --mount volume-driver=vieux/sshfs,source=cluster-volume,destination=/app,volume-opt=sshcmd=cloud_user@<STORAGE_SERVER_PRIVATE_IP>:/home/cloud_user/external,volume-opt=password=<PASSWORD> busybox cat /app/message.txt - Check the service logs to verify that the service is reading the test data from the external storage server.
docker service logs storage-service
Tag:Docker Swarm